Mute Swan
General Description
The Mute Swan is a very large, completely white bird with a long neck held in an S-curve. The bill is orange with a black knob at its base. Juveniles are gray or white, with the white morph more common.
Habitat
A native of Eurasia, the adaptable Mute Swan inhabits fresh- and saltwater ponds, coastal lagoons, and bays. It is often found in close association with people, but occasionally lives in remote areas as well.
Behavior
Mute Swans graze while walking on land, and feed on submergent, aquatic vegetation by reaching under the water with their long necks. They also adapt to feeding by humans. Highly territorial, males will aggressively defend their large territories against their own and other species, including humans, displaying, hissing, and attacking when provoked.
Diet
Mute Swans eat aquatic plant material, grasses, and waste grain. They also eat insects, snails, and other small aquatic creatures.
Nesting
Mute Swans usually form pairs at the age of two, but do not start breeding until their third or fourth year. The male gathers nesting material, and the female builds a shallow mound on a shoreline. The nest is large, five to six feet in diameter, and made of grasses and reeds with a shallow depression. The female performs most of the incubation of the four to six eggs, although the male will step in and allow the female to take breaks for foraging. Incubation lasts for about 36 days, and both adults tend the young, which sometimes ride on their parents' backs. The young begin to fly at 4 to 5 months but usually remain with the parents through the first winter.
Migration Status
Non-migratory in North America, Mute Swans may make short-distance, seasonal movements dictated by the weather.
Conservation Status
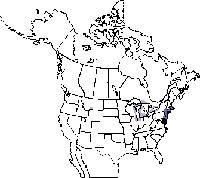
Domestic swans were first brought from Europe in the mid-1800s as an ornament for parks and estates. Feral populations have been established in much of the Northeast and in some parts of the Pacific Northwest. In the Northeast, many consider the Mute Swan a pest because it overgrazes ponds and excludes native waterfowl. Others consider it a beautiful addition to the avifauna, and much controversy has surrounded control efforts. Mute Swan populations in the Pacific Northwest—closely monitored by wildlife agencies—do not seem to be growing or expanding quickly, and thus have not yet become a management issue.
When and Where to Find in Washington
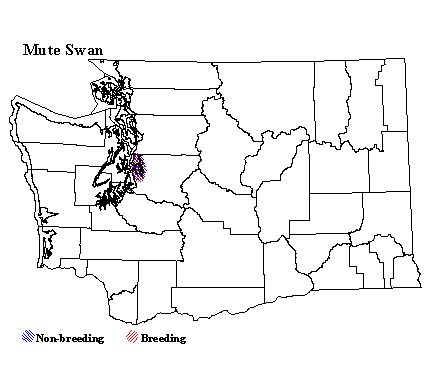
Mute Swans are very rare in Washington, but birds are occasionally sighted. These birds may be from populations in British Columbia. While no Mute Swans have bred in Washington in recent years, there are both captive and feral populations in southwestern British Columbia, and expansion into Washington is certainly possible. Mute Swans were first introduced in Vancouver around 1889, but the population did not become established until the 1950s. Winter-feeding and mild winters may be necessary for their survival. The only established feral population is on southern Vancouver Island from Duncan to Sooke. Humans providing food and shelter maintain other populations in the area, including Vancouver's Stanley Park and other urban ponds.
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map

Family Members
 Fulvous Whistling-DuckDendrocygna bicolor
Fulvous Whistling-DuckDendrocygna bicolor Taiga Bean-GooseAnser fabalis
Taiga Bean-GooseAnser fabalis Greater White-fronted GooseAnser albifrons
Greater White-fronted GooseAnser albifrons Emperor GooseChen canagica
Emperor GooseChen canagica Snow GooseChen caerulescens
Snow GooseChen caerulescens Ross's GooseChen rossii
Ross's GooseChen rossii BrantBranta bernicla
BrantBranta bernicla Cackling GooseBranta hutchinsii
Cackling GooseBranta hutchinsii Canada GooseBranta canadensis
Canada GooseBranta canadensis Mute SwanCygnus olor
Mute SwanCygnus olor Trumpeter SwanCygnus buccinator
Trumpeter SwanCygnus buccinator Tundra SwanCygnus columbianus
Tundra SwanCygnus columbianus Wood DuckAix sponsa
Wood DuckAix sponsa GadwallAnas strepera
GadwallAnas strepera Falcated DuckAnas falcata
Falcated DuckAnas falcata Eurasian WigeonAnas penelope
Eurasian WigeonAnas penelope American WigeonAnas americana
American WigeonAnas americana American Black DuckAnas rubripes
American Black DuckAnas rubripes MallardAnas platyrhynchos
MallardAnas platyrhynchos Blue-winged TealAnas discors
Blue-winged TealAnas discors Cinnamon TealAnas cyanoptera
Cinnamon TealAnas cyanoptera Northern ShovelerAnas clypeata
Northern ShovelerAnas clypeata Northern PintailAnas acuta
Northern PintailAnas acuta GarganeyAnas querquedula
GarganeyAnas querquedula Baikal TealAnas formosa
Baikal TealAnas formosa Green-winged TealAnas crecca
Green-winged TealAnas crecca CanvasbackAythya valisineria
CanvasbackAythya valisineria RedheadAythya americana
RedheadAythya americana Ring-necked DuckAythya collaris
Ring-necked DuckAythya collaris Tufted DuckAythya fuligula
Tufted DuckAythya fuligula Greater ScaupAythya marila
Greater ScaupAythya marila Lesser ScaupAythya affinis
Lesser ScaupAythya affinis Steller's EiderPolysticta stelleri
Steller's EiderPolysticta stelleri King EiderSomateria spectabilis
King EiderSomateria spectabilis Common EiderSomateria mollissima
Common EiderSomateria mollissima Harlequin DuckHistrionicus histrionicus
Harlequin DuckHistrionicus histrionicus Surf ScoterMelanitta perspicillata
Surf ScoterMelanitta perspicillata White-winged ScoterMelanitta fusca
White-winged ScoterMelanitta fusca Black ScoterMelanitta nigra
Black ScoterMelanitta nigra Long-tailed DuckClangula hyemalis
Long-tailed DuckClangula hyemalis BuffleheadBucephala albeola
BuffleheadBucephala albeola Common GoldeneyeBucephala clangula
Common GoldeneyeBucephala clangula Barrow's GoldeneyeBucephala islandica
Barrow's GoldeneyeBucephala islandica SmewMergellus albellus
SmewMergellus albellus Hooded MerganserLophodytes cucullatus
Hooded MerganserLophodytes cucullatus Common MerganserMergus merganser
Common MerganserMergus merganser Red-breasted MerganserMergus serrator
Red-breasted MerganserMergus serrator Ruddy DuckOxyura jamaicensis
Ruddy DuckOxyura jamaicensis

